Society of Environmental and Occupational Health

Society of Environment and Occupational Health
Protecting Environment and Promoting Occupational Health, Safety and Wellness

Society of Environment and Occupational Health
Protecting Environment and Promoting Occupational Health, Safety and Wellness













Slide 1
Slide 5
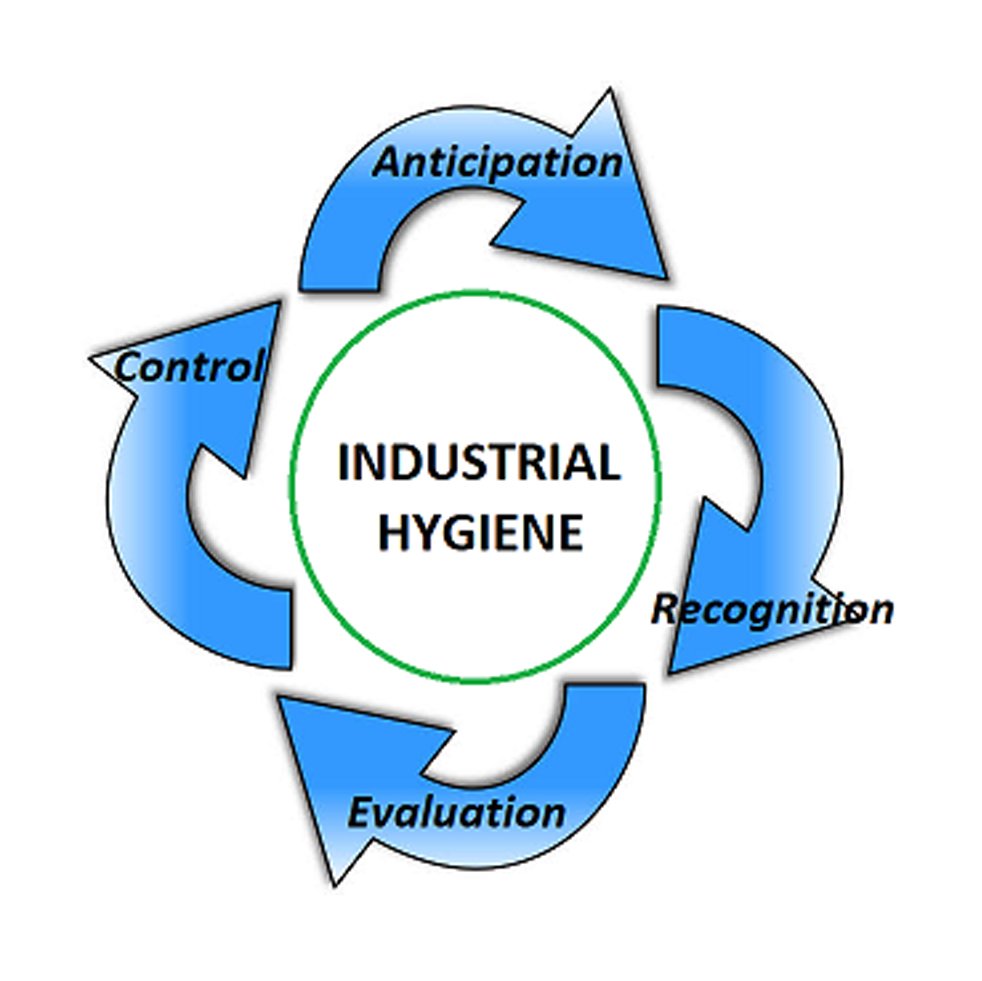
Construction Safety and Health
Slide 7
Climate Change-The Global Challenge
Slide 4
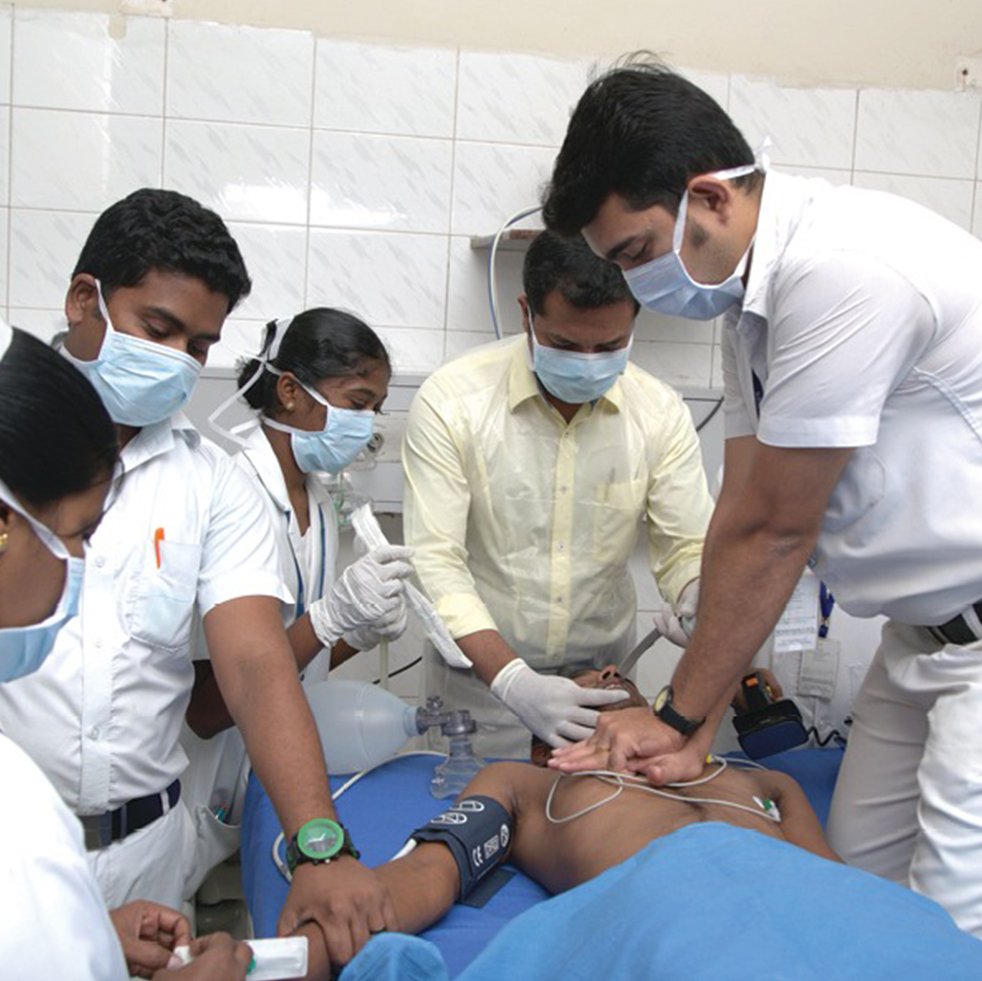
Food Safety and Hygiene
Slide 7
Slide 7
Slide 8
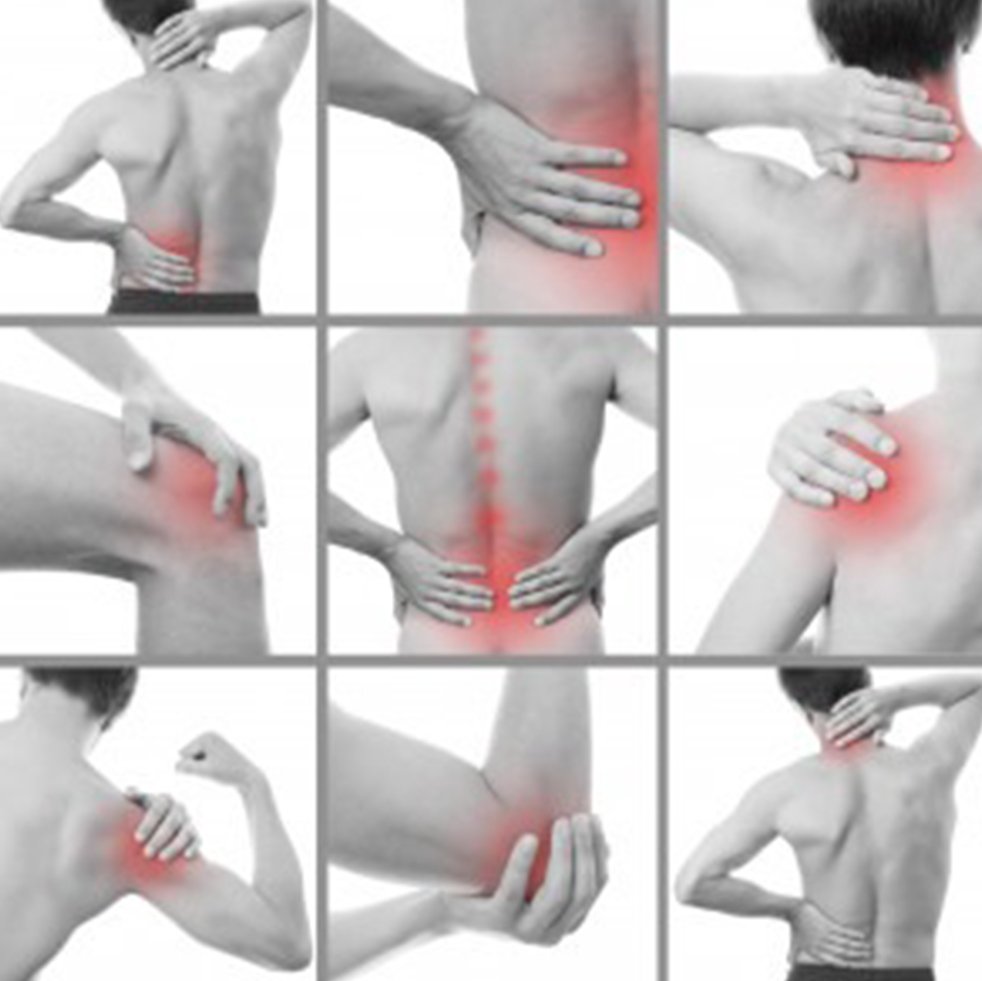
Office Ergonomics and Green Buildings
Slide 3
Nanotechnology and Pharmaceuticals
Slide 2
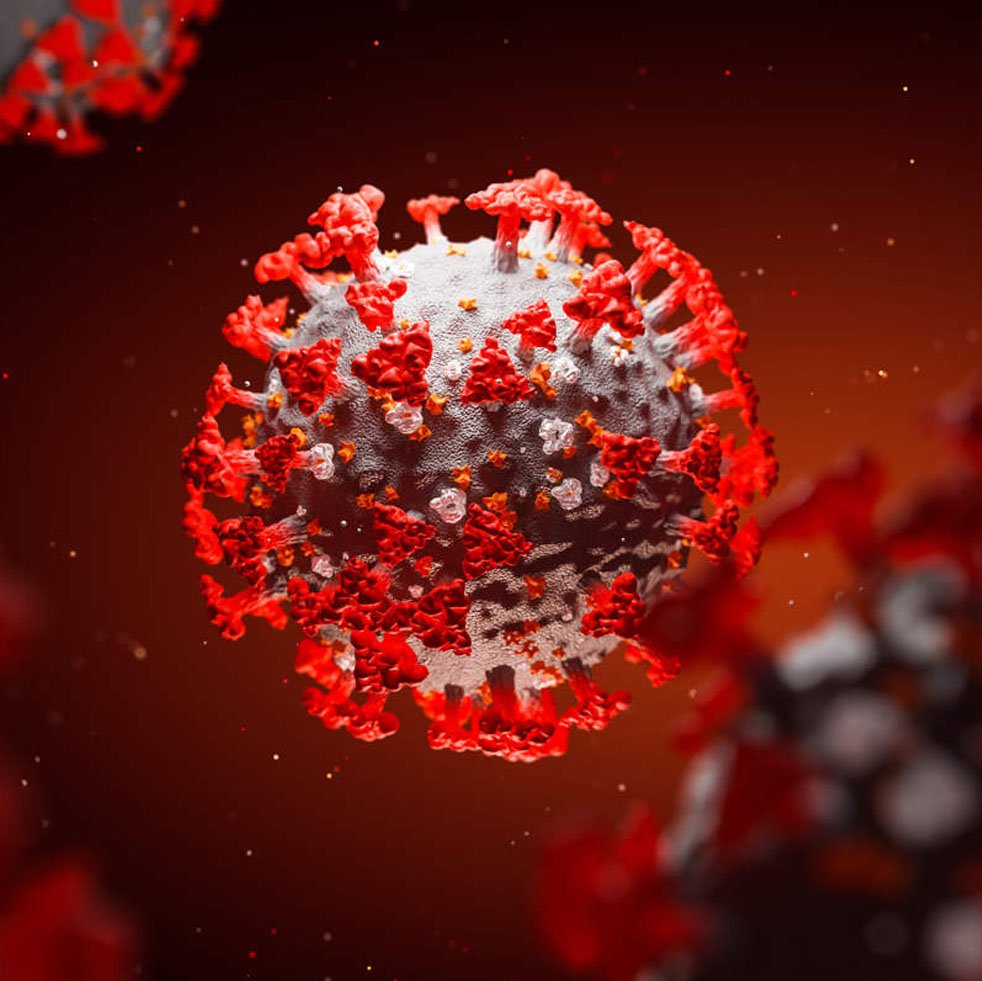
Covid 19 Pandemic
Slide 9
Travel Medicine &
international health regulations
Slide 6
Fitness and Wellness
Slide 6
Fitness and Wellness
Slide 6